Heat Sealing and ACF Bonding
Electrical conductive adhesives can be made between flexible and rigid circuit boards, glass panel displays and flex foils. In the heat sealing process the adhesive will be heated and cooled under pressure by means of a thermode (hot bar). Conductive adhesive can be obtained in the form of foil, flex or paste. This adhesive contains small conductive particles or spheres, which are separated by an isolating matrix of adhesive material.
Anisotropic Conductive Film
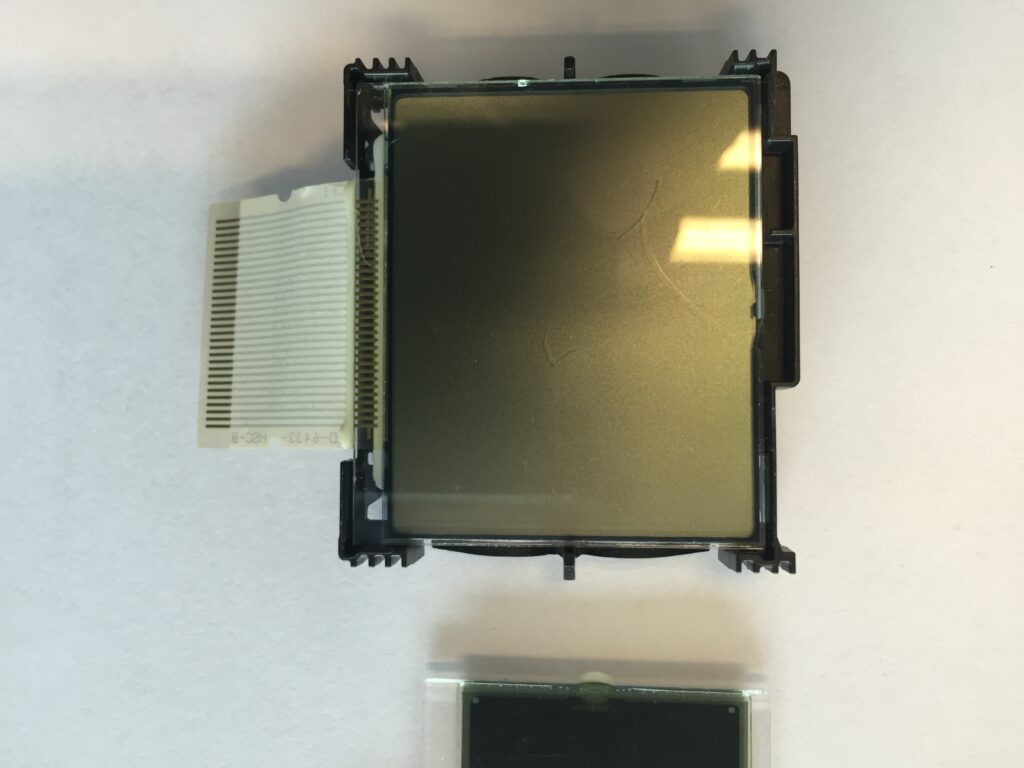
Anisotropic Conductive Film (ACF), is a lead-free and environmentally-friendly interconnect system to make electrical and mechanical connections between two components. ACFs are widely used to perform flex-to-board or flex-to-flex connections used in LCDs, handheld electronic devices such as mobile phones, smart watches, or in the assembly of CMOS camera modules.
ACF Laminating / Pre-Bonding
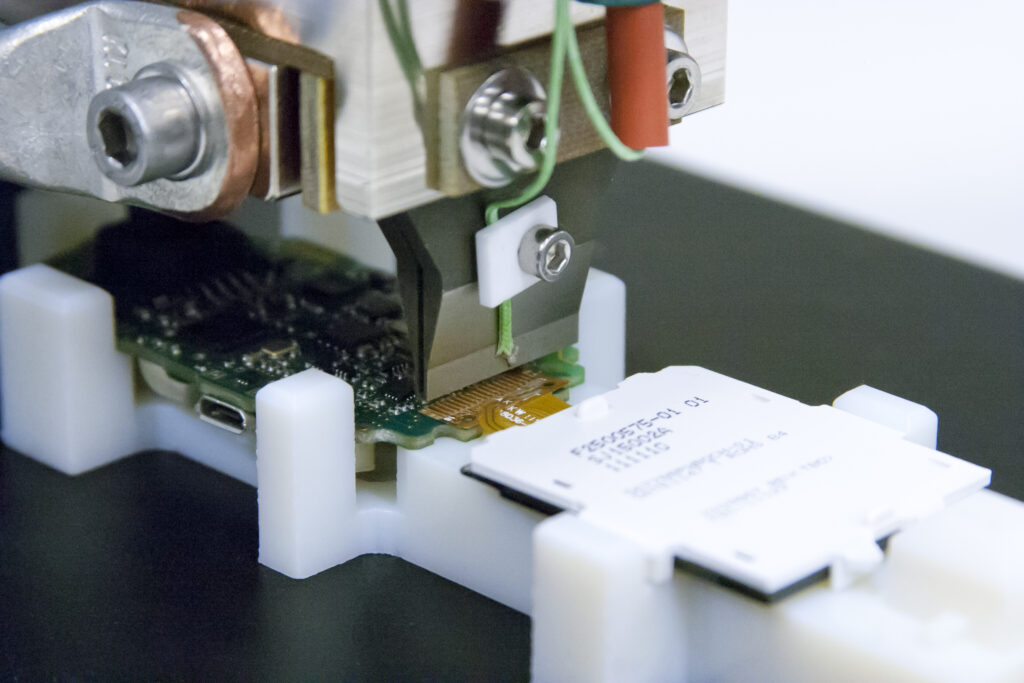
The ACF material is supplied as a reel and consists of adhesive filled with conductive particles and a protective layer. Prior to laminating (or pre-bonding) the ACF to the substrate, the ACF tape is pre-cut at the required length from the ACF reel. Cutting is done using the half-cut method where only the actual ACF material is cut, the cover-layer is used for tape transport. The ACF is now positioned over the bond surface, by placing the thermode (hot bar) on the ACF material, the material is transferred to the substrate.
Heat Sealing / ACF Final Bonding
(Also: Hot Bar Bonding, Pulsed Heat Bonding)
Once the ACF Laminating/Pre-Bonding process is completed the two parts to be joined are brought together in a fixture. This fixture (or jig) makes sure that the bonding parts fit perfectly together and ensured the repeatability of the process. Here flex or other parts can be aligned with great accuracy to match the traces on the substrate or other parts that need bonding. Now more temperature, time and pressure are applied and cause plastic deformation of the adhesive and compression of the particles. The particles that are trapped between the conductors form a conductive interface between the pads on the two mating surfaces and conduct only in the Z axis. Subsequent cooling and full curing of the adhesive while still in the compressed condition stabilize the joint.
Benefits ACF Bonding / Heat Sealing
- Lead-free process
- Smallest pitch >30 micron possible
- Flux free process
- Electrical connections to glass substrates
- No cleaning required after process
- Low process temperatures
Optimize Your Process with Heat Sealing and Conductive Adhesives
Ready to enhance your production with cutting-edge heat sealing and conductive adhesives? Contact us today to explore our innovative solutions and discover how we can optimize your bonding processes!
Applications ACF Bonding / Heat Seal Bonding